Which Describes How Electromagnetic Waves Travel
Torsional page 2 Waves. An electromagnetic metamaterial affects electromagnetic waves that impinge on or interact with its structural features which are smaller than the wavelength.
To behave as a homogeneous material accurately described by an effective refractive index its features must be much smaller than the wavelength.

. If a disturbance is parallel to the direction of travel of a wave the wave is classi ed as A. Lenzs law describes the direction of the induced field. Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831 and James Clerk Maxwell mathematically described it as Faradays law of induction.
They are not strongly absorbed. The video and text below describes some of the characteristics and uses of Radio waves and Microwaves. Therefore if any mechanism runs on electricity then it will always emit electromagnetic waves.
Antennas act as coupling points for electromagnetic energy to leave the guidance of wires for free space and visa versa. Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field. In doing so they generate a magnetic field.
Also electromagnetic waves can occur when even the smallest molecules of atoms or their nuclei move. And every sound we hear is a wave. Only energy not matter is transferred as a wave moves.
Light waves travel across the universe allowing us to see distant stars. Citation neededFor microwave radiation the features are on the order of. The substance that a wave moves through is called the medium.
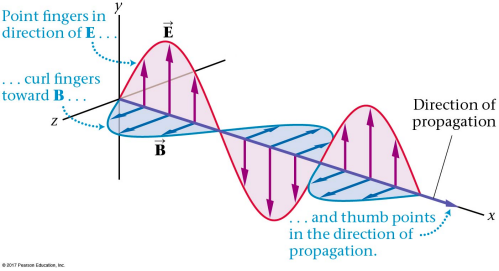
Electromagnetic waves arise during the accelerated movement of electrical charges. Electromagnetic waves are characterized on the basis of their respective energy E frequencies f and wavelengths λ. They are produced when an alternating current flows in an aerial and they spread out and travel through the atmosphere.
EM waves can travel without the guiding action of wires. A wave is a disturbance that moves energy from one place to another. Radio waves are the lowest-energy lowest-frequency and longest-wavelength electromagnetic waves.
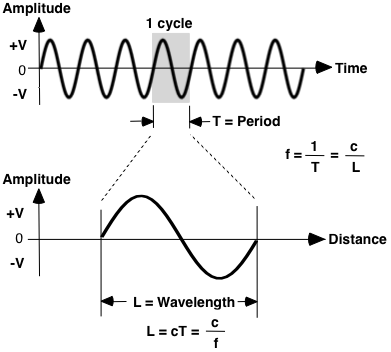
So what do all these different waves have in common. The graph shown represents the displacement of a point in a medium as a function of time when a wave passes through the medium. The area near this coupling activity is exactly where compliance officers have.
F requency describes how. What is the frequency of the wave. This happens when they.
The points where EM waves leave the guiding influence of wires and move to free and unbounded travel are called antennas.

Learn About Electromagnetic Waves Chegg Com

Anatomy Of An Electromagnetic Wave Science Mission Directorate

The Electromagnetic Spectrum And Its Domains The Abscissa Highlights Download Scientific Diagram
What Is An Electromagnetic Wave Quora

Physical Science Light Physical Science Absent Students Science

Nikola Tesla For The First Time Describes His New System For Supplying Wireless Power To Run All The Earth S Industries Nikola Tesla Tesla Tesla Inventions

Visible Light Spectrum Poster Visible Light Spectrum Visible Light Electromagnetic Spectrum
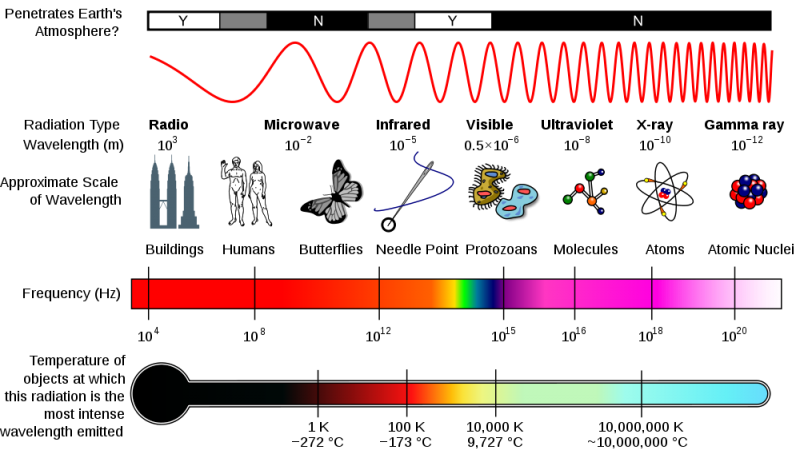
What Is The Electromagnetic Spectrum Space Earthsky

The Highest Part Of A Wave Is Called A Crest The Lowest Part Is The Trough Homeschool Science Waves 8th Grade Science

Sound The Science Of Waves How They Travel How We Use Them Physics Lessons Physics Classroom Ap Physics

Electromagnetic Waves Spectrum Cornell Doodle Notes Distance Learning Science Teaching Resources Doodle Notes Distance Learning
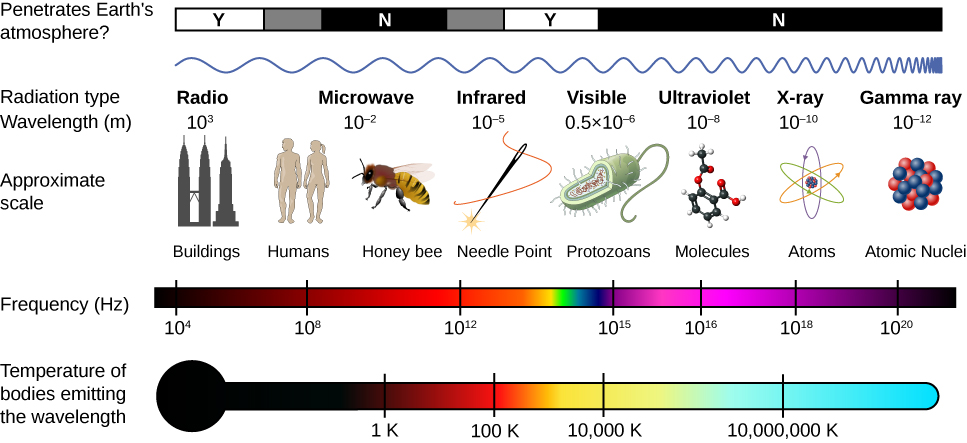
The Electromagnetic Spectrum University Physics Volume 2

The Electromagnetic Spectrum Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible Light Spectrum Spectrum

Electromagnetic Waves Ck 12 Foundation

Radiation Easy Science Science Flashcards Chemical Energy Radiation